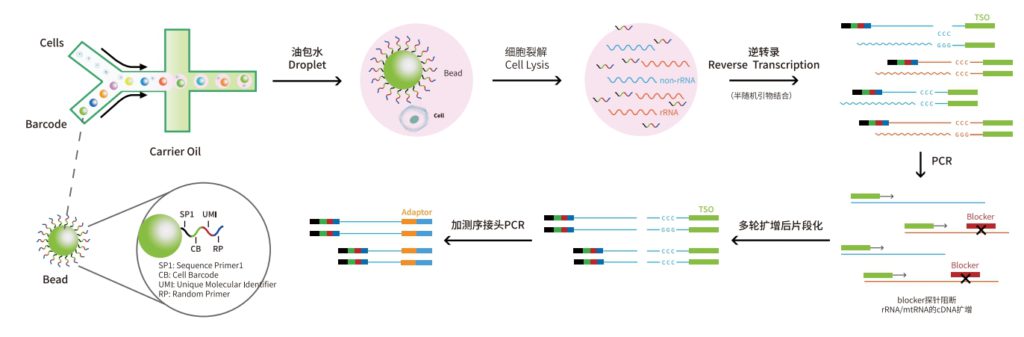
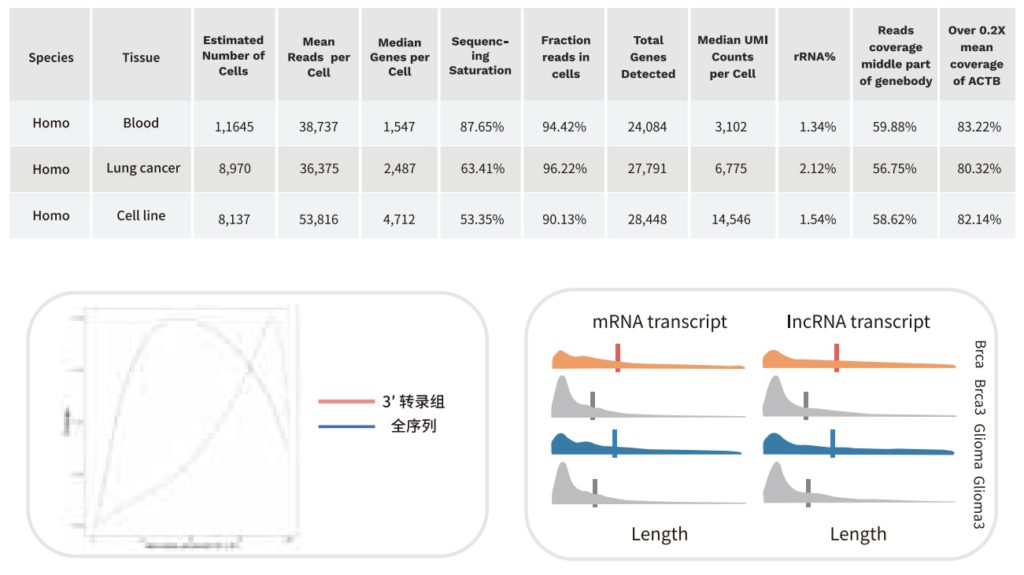
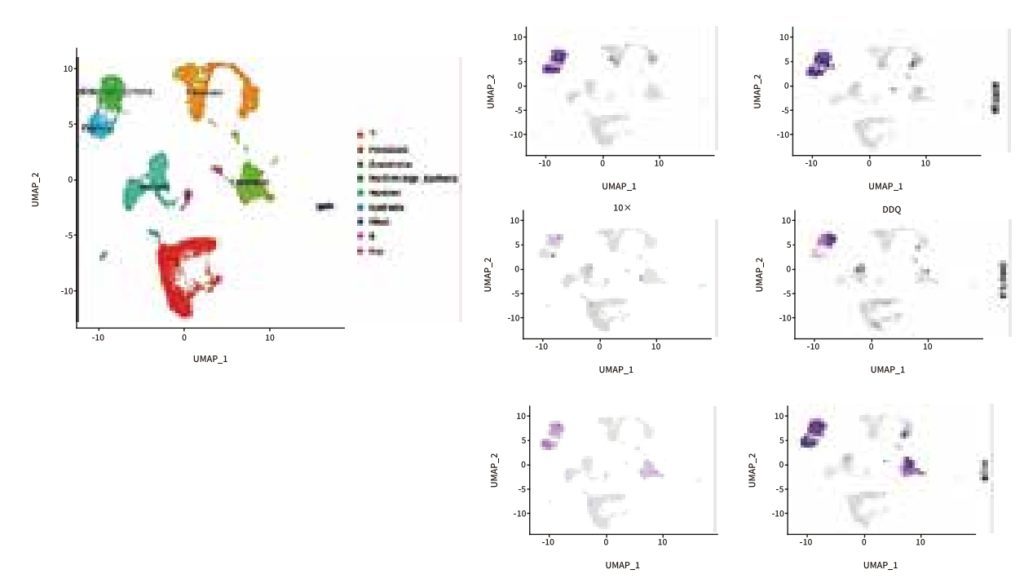
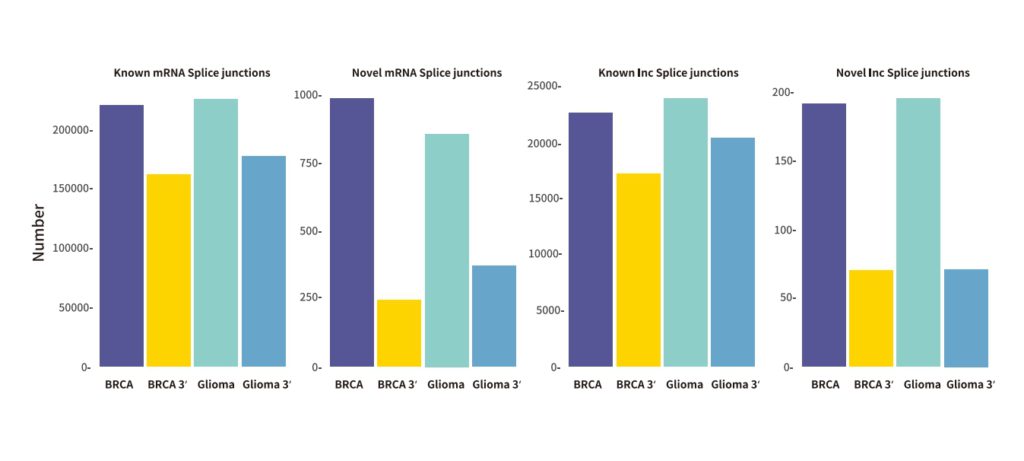
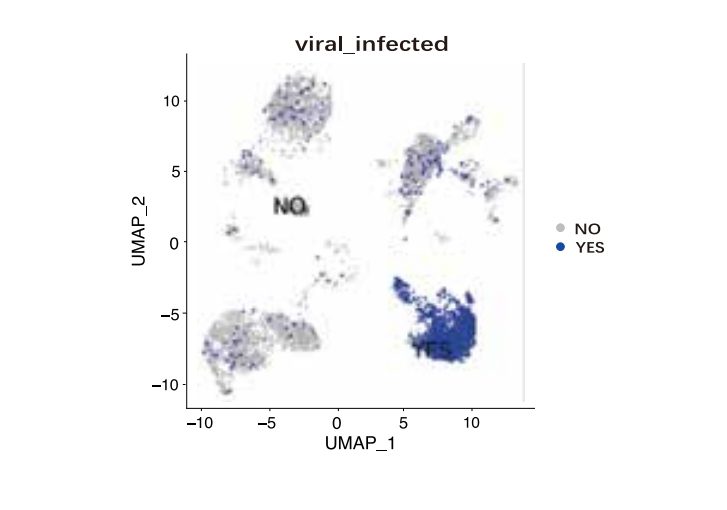
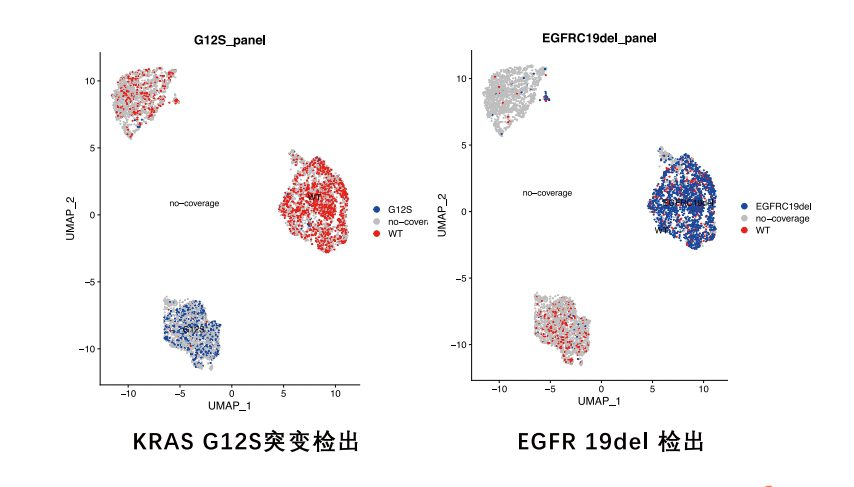
The single-cell full-length transcriptome detection technology, scFAST-seq, uses semi-random primers 12N7K to capture RNA, replacing the method of using olig0-dT to capture RNA. This enables reverse transcription to be initiated at multiple sites of the transcript, achieving full-length coverage of RNA. Meanwhile, by using blockers to block mitochondrial ribosomal RNA (mt-rRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), data waste is reduced, and information on some non-coding RNAs other than mRNA can be effectively obtained. Thanks to the above technological improvements, the scFAST-seq technology has unique advantages in mutation detection, the detection of lncRNAs (long non-coding RNAs), and the detection of alternative splicing events.
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文