introduction
RNA-binding proteins regulate various stages of the RNA life cycle, including splicing, cleavage, polyadenylation, stabilization, localization, editing and translation. The interaction between RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and RNA is the key to the regulation of the transcriptome and proteome. The loss of their functions leads to disorders in the body and triggers a variety of diseases. The systematic identification of the dynamic changes of RBPs in cell functions and disease states is of great significance for researchers to understand physiological functions and disease progression.
In 2009, the team led by Professor Gene W. Yeo from the University of California, San Diego, successfully constructed the RNA map of the cell type-specific splicing regulator FOX2 in human embryonic stem cells through a technique called cross-linking immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing (CLIP-seq). CLIP-seq is a powerful experimental technique that can bind specific RNA molecules to protein complexes with high specificity, thus revealing the functions and regulatory mechanisms of RNA molecules in cells.
On March 28, 2016, Nature Methods published an article titled “Robust transcriptome-wide discovery of RNA-binding protein binding sites with enhanced CLIP (eCLIP)”, introducing a new CLIP technique – enhanced CLIP (eCLIP). Since reverse transcription usually terminates at the RNA-RBP cross-linking sites, eCLIP connects single-stranded DNA adapters to the 3′ end of cDNA fragments after reverse transcription, and uses reverse transcription primers and single-stranded DNA adapters to amplify to obtain sequencing libraries. It completely retains those RNA molecules that terminate at the RNA-RBP cross-linking sites and achieves single-base resolution by analyzing UV cross-linking sites. In addition, the eCLIP method has also improved the use of size-matched Input (SMInput) as a negative control. The eCLIP technique provides a powerful tool for in-depth research on the interaction between RNA and proteins.
Wuhan Ruixing has independently developed and optimized the RNA library construction strategy in eCLIP, improved the ligation efficiency of the adapters at both ends of RNA in eCLIP, simplified the operation steps and increased the success rate of library construction.
advantages
✔ High resolution: Achieving single-base resolution.
✔ High signal-to-noise ratio: The Input samples effectively remove the background noise generated by the system.
✔ Simple process: Optimize the library construction steps and improve the success rate.
workflow
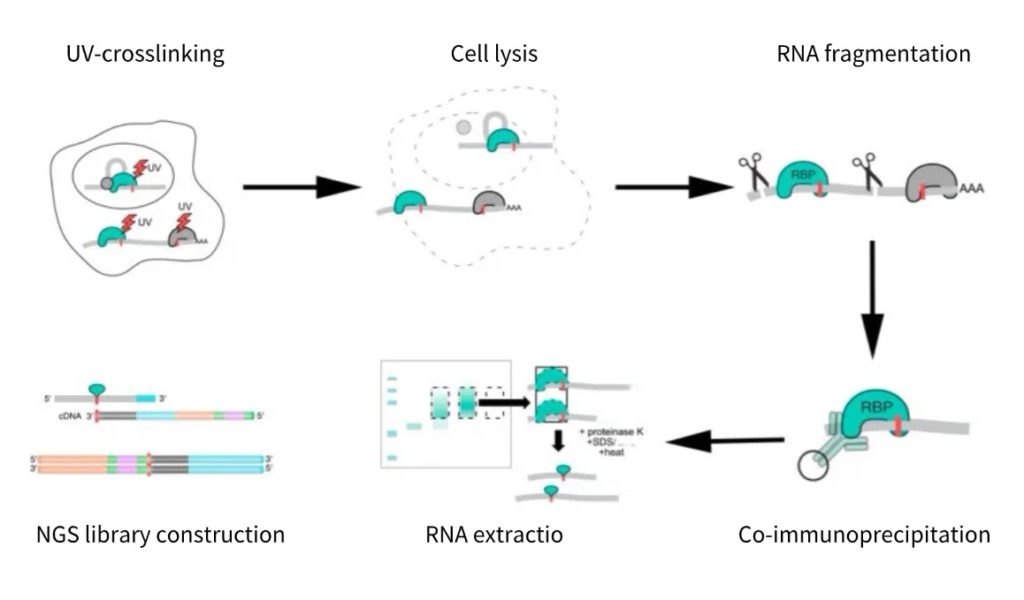
1) UV-crosslinking
2) Cell lysis
3) RNA fragmentation
4) Co-immunoprecipitation
5) NuPAGE gel electrophoresis
6) RNA extraction
7) RNA library construction
Research Cases
Topoisomerase I (TOP1, Topoisomerase I) is an important enzyme that can promote DNA relaxation and prevent and eliminate torsional stress during the transcription process. However, the mechanisms behind the regulation of the activity of TOP1 enzyme are still unclear to researchers at present. Recently, a research report titled “RNA interacts with topoisomerase I to adjust DNA topology” was published in the international journal Molecular Cell.

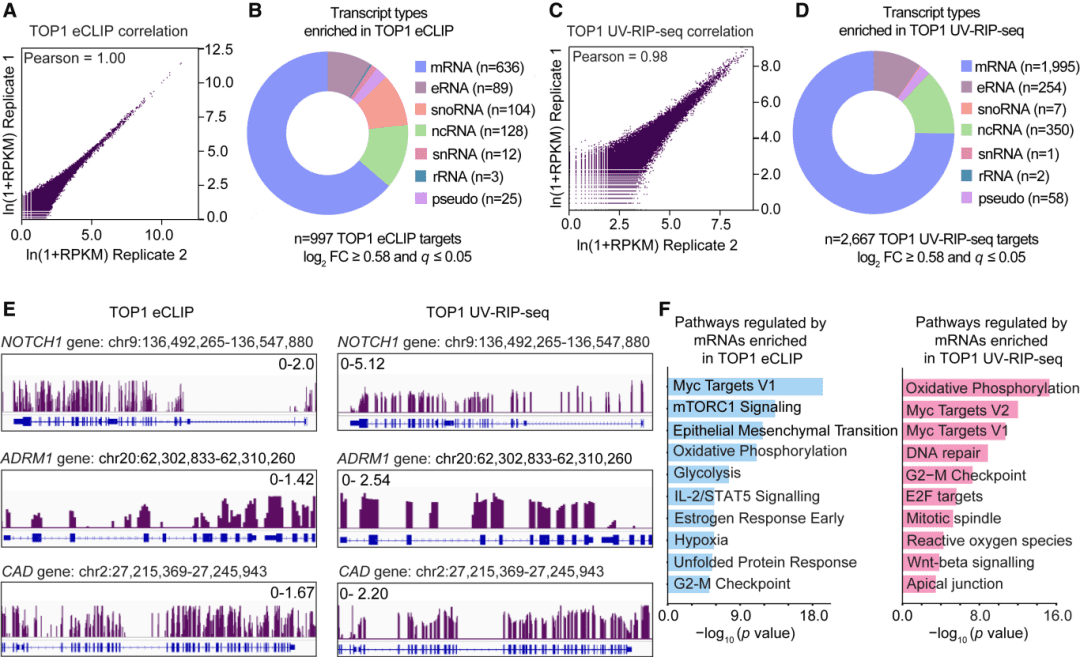
Scientists from Northwestern University and other institutions in the United States combined the eCLIP sequencing technology with in vitro RNA binding assays. The researchers found that TOP1 can bind to RNA, and most of these RNAs are mRNAs, which can carry the genetic information required for protein synthesis. Next, through research, the researchers gained a better understanding of why the binding of TOP1 to RNA is related to its important role in relaxing DNA. By using DNA supercoiling experiments, single molecule magnetic tweezer assays, and advanced sequencing methods, the researchers analyzed the catalytic activity of TOP1 and how it supports the interaction between DNA and RNA.
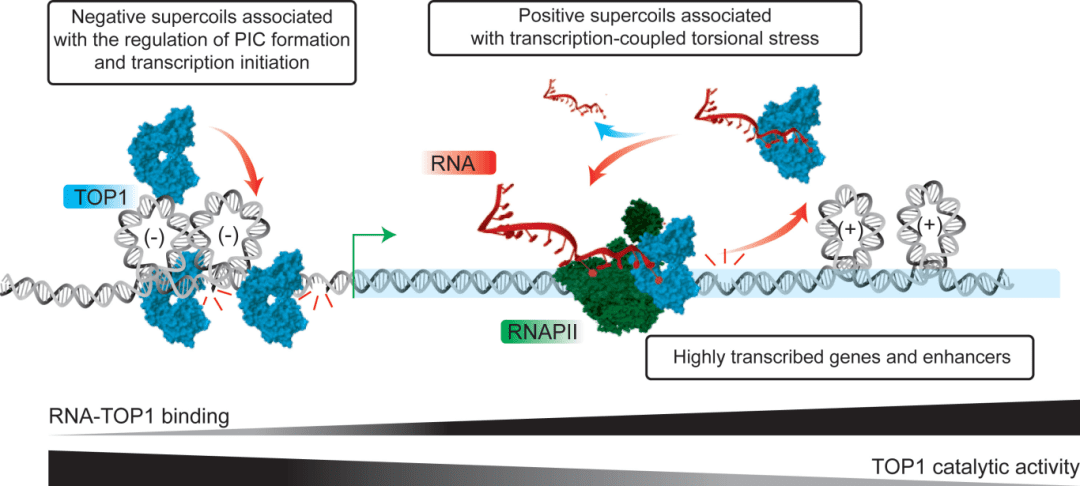
The researchers found that RNA acts contrary to the activity of TOP1. Importantly, however, RNA polymerase II (a multi-protein complex that can transcribe DNA into mRNA) can activate the transcription process. Researcher Mannan Bhola said that this study has revealed a unique mechanism in which RNA can regulate TOP1-mediated DNA relaxation and thus play an important role in regulating the gene transcription process. By identifying that TOP1 can act as an RNA-binding protein, the researchers have provided new insights into the interaction between RNA and DNA during transcription.
Reference
【1】Yeo, G., Coufal, N., Liang, T. et al. An RNA code for the FOX2 splicing regulator revealed by mapping RNA-protein interactions in stem cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16, 130–137 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1545.
【2】Van Nostrand, E., Pratt, G., Shishkin, A. et al. Robust transcriptome-wide discovery of RNA-binding protein binding sites with enhanced CLIP (eCLIP). Nat Methods 13, 508–514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3810.
【3】Bhola, Mannan, et al. “RNA interacts with topoisomerase I to adjust DNA topology.” Molecular Cell (2024).
