RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
The m6A modification is widely present in human transcriptome RNA. Current research shows that more than 7,000 mRNAs and 300 long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) contain this modification. This modification is enriched and distributed near the stop codons and in the 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of mRNAs, suggesting that the m6A modification has important regulatory functions. Many m6A modification sites are conserved between humans and mice, and the modification levels of certain m6A modifications also change constantly during different developmental stages, which also implies their important regulatory functions.
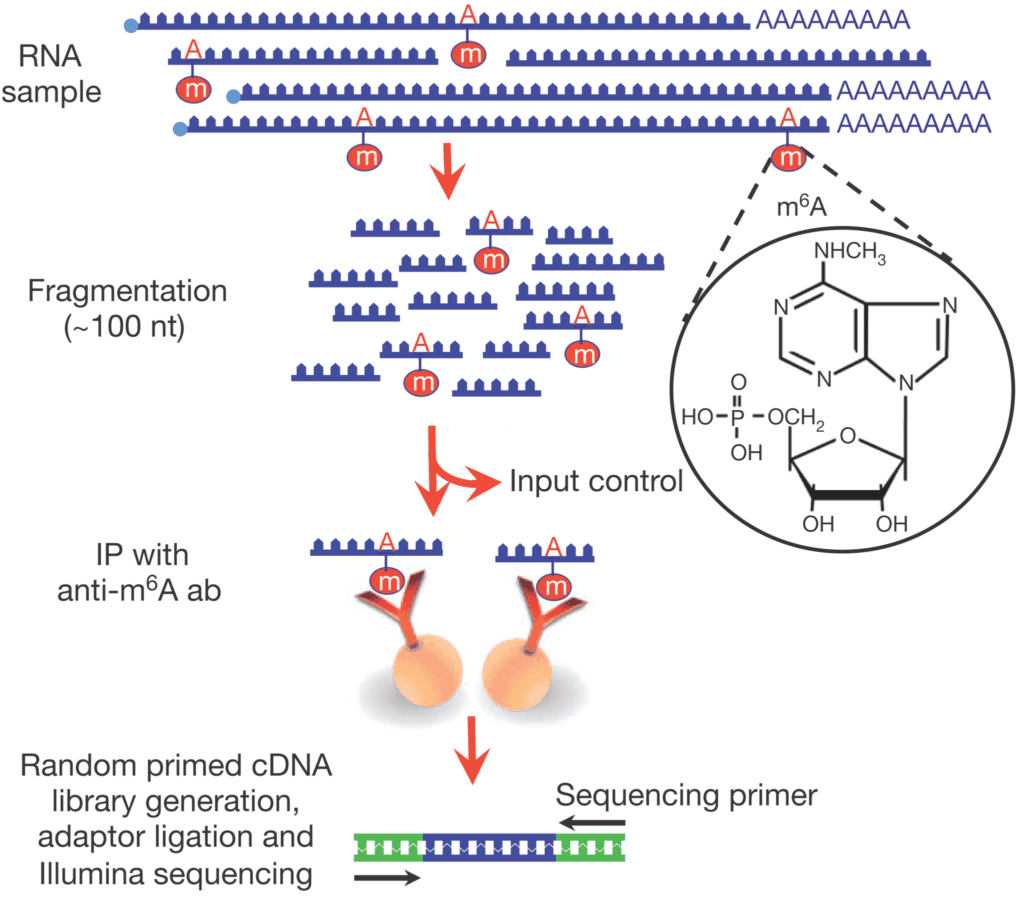
Currently, the genome-wide research method for m6A is methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (meRIP-seq). Its principle is to conduct immunoprecipitation on RNA fragments with m6A modification in cells by using antibodies that specifically recognize m6A modification. Through high-throughput sequencing of the precipitated RNA fragments and then combined with bioinformatics analysis, the status of m6A modification can be systematically studied on a genome-wide scale.
✔ Provide personalized solutions for different research fields.
✔ The analysis process is comprehensive, the data interpretation is detailed, and personalized analysis can be provided for later data mining.
✔ Incorporate multiple peak analysis strategies, including two methods: Ablife and Piranha.
✔ Rich research ideas: analysis of the m6A modification landscape and modification characteristics, identification of differential m6A modification sites and genes among different experimental groups; combined analysis with RNA-seq, CLIP-seq data, etc. to reveal the functions of m6A modification.
-1024x380.png)

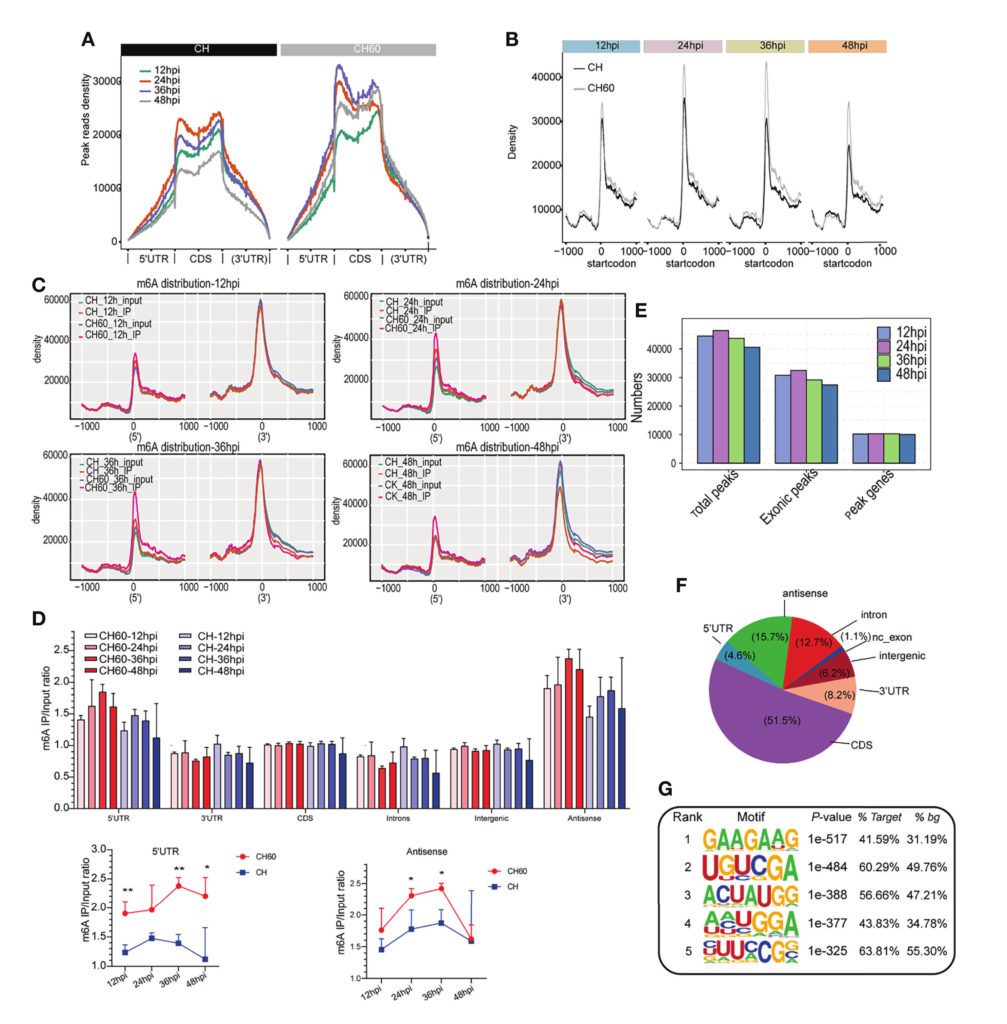
By performing m6A-seq sequencing on the liver tissues of ducklings infected with highly virulent and weakly virulent duck hepatitis A virus (DHAV), the m6A modification levels and distribution characteristics on duck mRNA were analyzed for the first time. It was found that GAAGAAG was the most abundant motif among the modification motifs. Through integrated analysis of m6A-seq and RNA-seq data, it was discovered that m6A was generally positively correlated with the mRNA expression levels in the livers of ducklings infected with DHAV (Wu et al., 2022).