RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
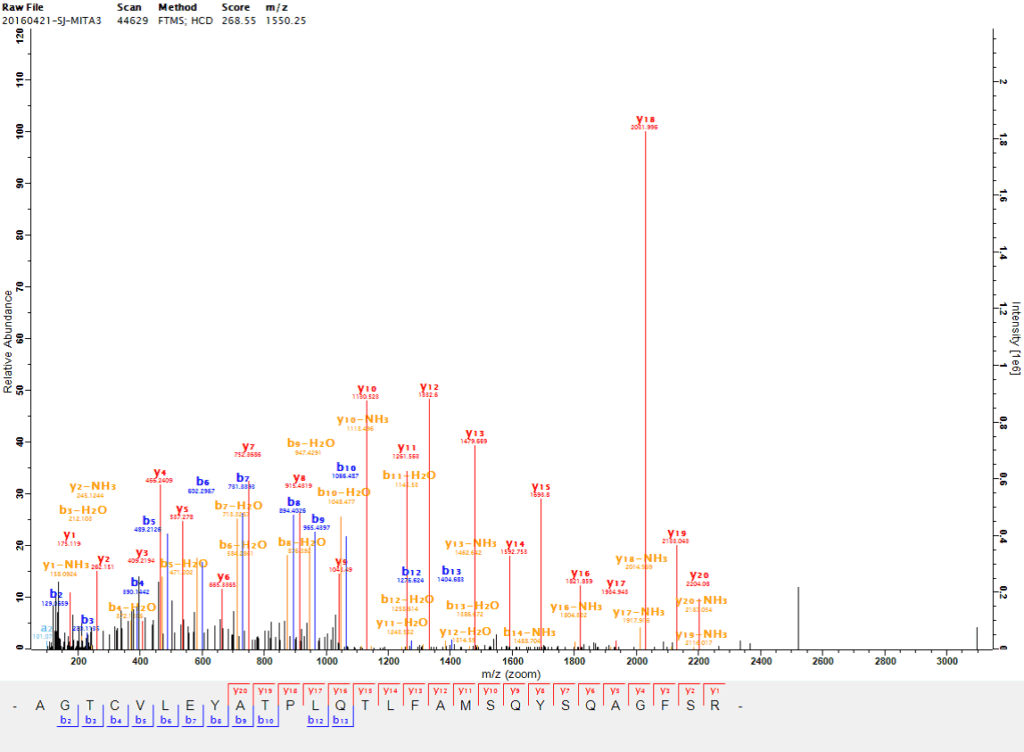
Proteins undergo post-translational modifications, and phosphorylation modification is one of the important post-translational modifications of proteins. Through phosphorylation modification, the activity of proteins can be regulated and the signal transduction process can be affected. After enriching phosphorylated peptides or proteins by means of the affinity of phosphate groups for metals, combined with high-throughput liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), the sites of phosphorylated peptides can be detected. Since phosphorylation modification is widely involved in various physiological and pathological processes, the phosphoproteome is applicable to research fields such as disease research, growth and development, and plant stress resistance.
✔ High specificity and good enrichment efficiency.
✔ High-throughput identification of phosphorylated peptides and proteins.
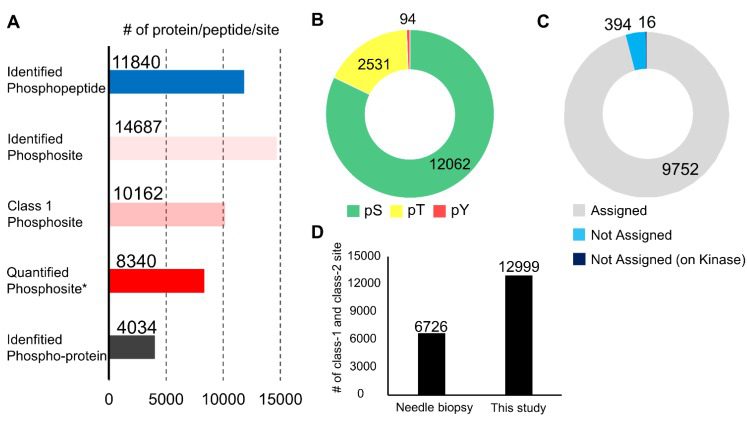
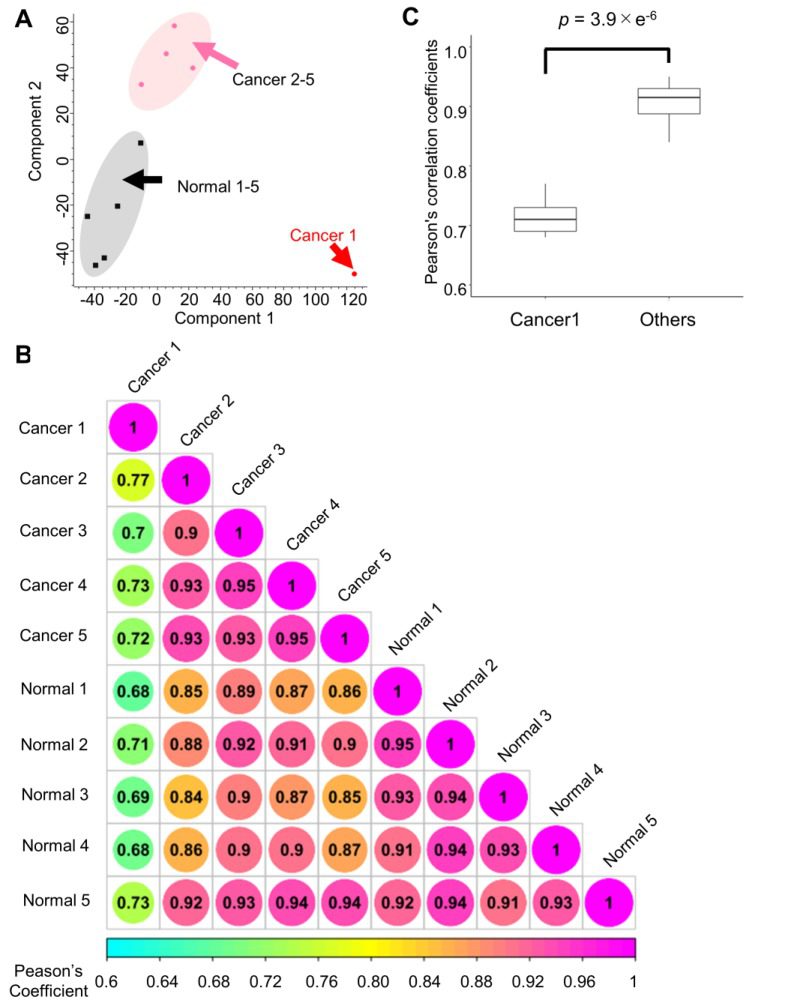
In this study, the authors conducted sequencing analysis and verification on samples from endoscopic biopsies of gastric cancer through phosphoproteome sequencing, which was used to monitor the activity of therapeutic kinases and had higher sequencing abundance and sensitivity compared to surgical samples. After excluding cases that deviated from the sample group, the researchers identified 4,034 phosphoproteins and 14,687 phosphorylation sites from the endoscopic biopsy samples, which was twice the number of sites identified in previous phosphoproteomic studies on needle biopsy samples, indicating that the analytical method used in this study had a high identification depth. By comparing samples from cancerous tissues and normal mucous membranes, the study found that there were significant differences in phosphorylation signals between the two. Pathways related to the DNA damage response (DDR) were significantly enriched in cancerous tissues, suggesting that endoscopic biopsy can accurately reflect the oncogenic phosphorylation signals of cancer cells in tissues.