RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
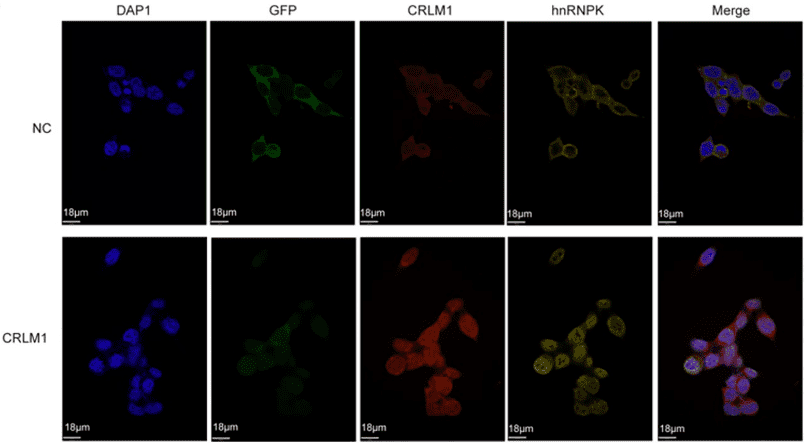
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a technique that utilizes fluorescence-labeled specific nucleic acid probes to hybridize with the corresponding target DNA molecules or RNA molecules inside cells. By observing the fluorescence signals under a fluorescence microscope or a confocal laser scanner, it can determine the morphology and distribution of the cells or organelles that are stained after hybridization with specific probes, or locate the DNA regions or RNA molecules that have combined with the fluorescence probes within chromosomes or other organelles.
✔ Strict controls and experimental quality control points to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
✔ Data analysis, graphing and English materials and methods, along with detailed raw data, will safeguard the authenticity of your data and facilitate your article publication.
✔ Published article cases.

Delivery Contents:
A. Raw data of all experimental results.
B. Experimental reports (including detailed experimental procedures and the manufacturer and catalog number information of the main instruments and reagents).
C. English materials and methods.