introduction
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification in which DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) add methyl groups to cytosine nucleotides to form 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), usually inhibiting gene transcription. CpG islands are common regions in gene promoter areas, and methylation affects protein binding and gene expression. Researchers use bisulfite sequencing technology (BS-seq) and reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) technology to identify methylation sites. BS-seq requires a large amount of data, while RRBS covers about 1-5% of CpG sites in the genome.
Nanopore sequencing technology can directly detect the methylation status of cytosine (for example, at CpG sites) without the need for bisulfite conversion. CpG sites are usually densely distributed in regions called CpG islands (CGIs), and the promoters of most vertebrate genes are located within these CGIs. Changes in the methylation patterns within promoters are closely related to gene expression and disease states such as cancer: Studying the methylation differences between tumor samples and normal samples helps to reveal the mechanisms related to tumor formation and development. Adaptive sampling (AS) provides a fast, flexible, and accurate method to enhance the coverage of regions of interest (such as cgi) by preferentially consuming non-target areas during the sequencing process. The RRMS protocol enables users to sequence 310 Mb of the human genome that is rich in CpG, including all annotated CpG islands, shores, shelves, and over 90% of promoter regions (100% of promoters contain more than 4 CpG). In addition, it also includes other CpG-rich regions in the genome. The total number of CpG sites recorded in the.bed file reaches 7.18 million.
advantages
✔ Simple and convenient: No need for conversion with chemical reagents or treatment with restriction endonucleases.
✔ High coverage: The targeted sequencing region for humans is 310 M, and that for mice is 308 M.
✔ Multiple methylation modifications: 5mC, 5hmC, 6mA, 4mC, etc.
✔ Variant analysis: It can analyze relevant information such as CNV (Copy Number Variation), SV (Structural Variation) and SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism).
✔ Single-base resolution: It can detect at the single-base level.
workflow
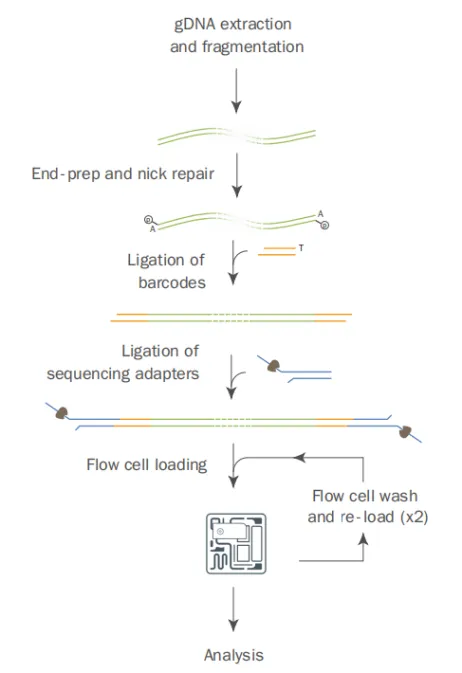
The DNA-reduced representation methylation multiplex sequencing (RRMS) technique first extracts genomic DNA samples and then fragments the DNA. After fragmentation, the average length of the DNA is 6 kb. The ends of the fragmented DNA are repaired and sequencing adapters are ligated. Then, the RRMS adaptive sampling sequencing program is selected on the ONT sequencing instrument.
Research Cases
The research team from the University of Pennsylvania in the United States has developed an analysis pipeline for long-read genomic DNA methylation adaptive sampling sequencing. The research results were published in Nature Communications, and the article was titled “A signal processing and deep learning framework for methylation detection using Oxford Nanopore sequencing”.

Oxford Nanopore sequencing can detect DNA methylation and has unique advantages. Adaptive sampling reduced representation methylation sequencing is applicable to CpG islands or imprinted regions. DeepMod2 is a deep learning framework that utilizes the ionic current signals of nanopore sequencing to detect DNA methylation. DeepMod2 runs efficiently on CPUs and can infer epigenetic haplotypes or methylation calls. Compared with the closed-source tools Guppy and Dorado, DeepMod2 has comparable performance. In conclusion, DeepMod2 is a fast and accurate open-source DNA methylation detection tool.
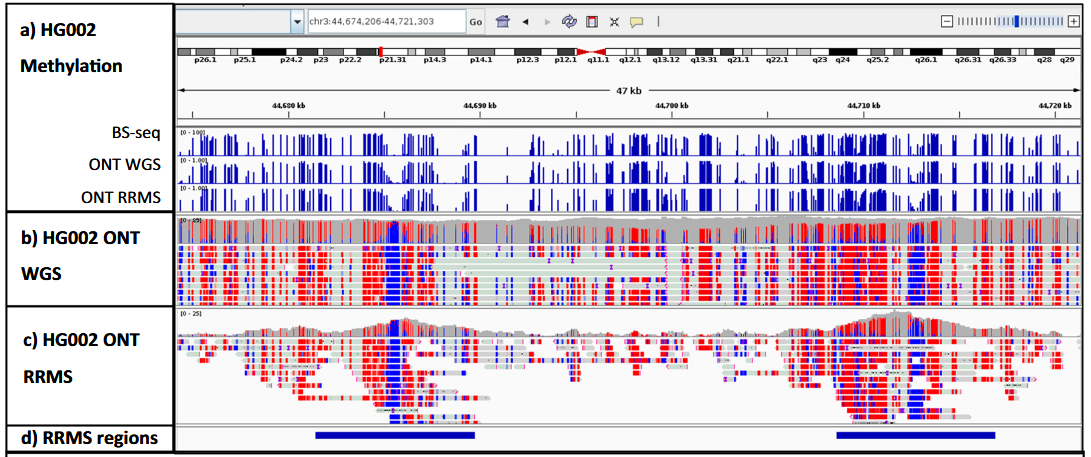
The figure shows the IGV (Integrative Genomics Viewer) plots of reads and methylation calls for whole-genome and RRMS (Reduced Representation Methylation Sequencing) nanopore sequencing, and compares the coverage of RRMS reads. Using DeepMod2, the authors detected 5mC in HG002 RRMS and found that 39 cytosines were detected within the whole-genome CpG motifs and 1399 were detected within the target regions. After aggregation, 248 CpG sites were detected across the whole genome and 717 were detected within the target regions. The number of aggregated CpG sites detected in the RRMS regions is more than that of stranded CpG sites, and the number of the latter is less than twice that of the former.
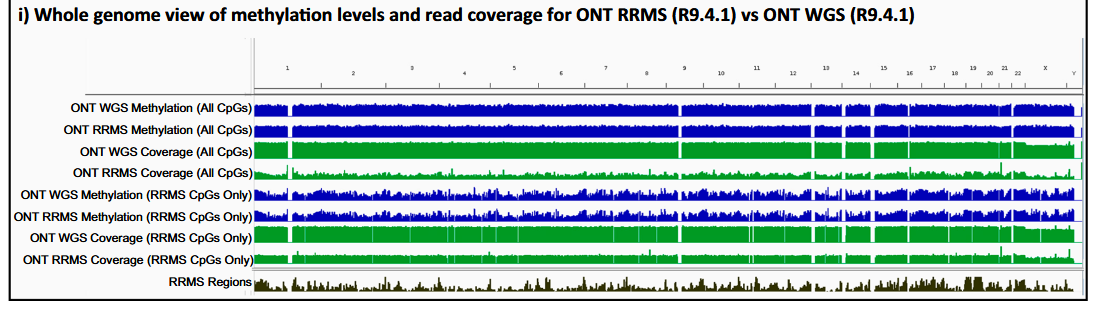
The figure displays the coverage and methylation levels of the ONT RRMS (Oxford Nanopore Technologies Reduced Representation Methylation Sequencing) and WGS (Whole Genome Sequencing) datasets, as well as the tracks of RMMS CpGs (Reduced Representation Methylation Sequencing Cytosine-Phosphate-Guanine sites) and all CpGs and the tracks of the RRMS target regions. The enrichment of the RRMS target regions relative to the off-target regions can be observed, as indicated by the coincidence of the RRMS tracks and the coverage peaks.
Reference
【1】 Ahsan, M.U., Gouru, A., Chan, J. et al. A signal processing and deep learning framework for methylation detection using Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Nat Commun 15, 1448 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45778-y
